Campaign Toolkit

Clinical Support: Level 2
Equip staff with standing orders
Build support throughout the organization for standing orders to increase efficiency in administering adult vaccinations. Develop and implement standing orders in accordance with state regulations and based on organizational priorities and need. Evaluate and maintain standing orders annually and when changes in vaccine recommendations and guidelines arise.
Standing orders allow appropriately trained healthcare professionals (as determined by state laws) to assess immunization status and administer vaccines to qualifying patients outside of a clinical exam and without a provider present.
With standing orders, healthcare teams can streamline their workflows and administer vaccines more efficiently. Standing orders have been shown to improve immunization rates across a range of settings and populations. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention’s (CDC) Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP) specifically recommends them for influenza and pneumococcal vaccinations.1
To develop and implement standing orders in your organization, follow the steps below.
Step 1:
Build support and determine priorities
-
Identify what standing orders may already exist in your organization. Gather lessons learned from colleagues that will help inform the development of a standing order for influenza, pneumococcal, Td/Tdap, zoster, RSV, COVID-19, and/or hepatitis B vaccinations.
-
Engage leadership in discussions around the value of standing orders for routine adult immunizations. Emphasize how standing orders increase efficiency and reduce physician workload.
-
Consult your state licensing and scope of practice guidelines. Every state has unique requirements for who is authorized (e.g., RNs, LPNs, MAs, etc.) to complete certain clinical tasks (e.g., administering a vaccine) via a standing order.
-
Consider if clinical judgment will be needed. If clinical judgement is needed to implement the standing order, it may impact which staff should be responsible for its execution (i.e., a licensed nurse rather than a medical assistant).
-
Determine priorities. It may be more efficient to tackle development of a standing order for one vaccine at a time. If you don’t already have a standing order for influenza vaccinations, consider starting with a standing order for influenza since this vaccine is administered widely on an annual basis.
-
Create a plan to educate and gather feedback from all stakeholders affected by the standing order. It is essential to gain buy-in from physicians since standing orders are performed under the signing physician’s name. Develop talking points to address provider and staff concerns (e.g., to maximize staff comfort, standing orders will be regularly reviewed and updated to reflect current guidelines).
Step 2:
Develop and refine your standing order(s)
Whether updating existing standing orders or writing new ones, every standing order for vaccinations should include content that explains how to:
-
Determine vaccine eligibility
-
Choose the correct vaccine when there are multiple options
-
Administer the vaccine correctly and safely
-
Document vaccinations in the patient record and registry
-
Manage medical emergencies
-
Report adverse events
Standing orders for vaccinations should also include:
-
The vaccine name and schedule
-
Needle size and dosage
-
Administration procedures
-
Indications, contraindications, and precautions
-
Federally required information such as a Vaccine Information Statement
There is a template standing order for many of the campaign measures included in the tools below.
Step 3:
Integrate standing orders into clinical practice
Each physician will have to formally sign off on the standing order, agreeing to have their staff perform the actions outlined by the standing order under their name and license. To ensure smooth implementation, educate all providers and clinic staff on the new standing order, including purpose, changes in workflow, and impact on individual roles.
Step 4:
Maintain standing orders for efficiency, safety, and success
Store standing orders with other medical protocols and make copies readily available for relevant staff. Be sure to review your standing orders on an annual basis. Consult your Immunization Champion to ensure the orders reflect the latest relevant CDC’s ACIP guidance.
1 Modlin, J.F., Snider, D.E., et. Al. Use of Standing Orders Programs to Increase Adult Vaccination Rates. MMWR Recommendations and Reports 2000;49(RR01):15-26. Retrieved from https://www.cdc.gov/mmwr/preview/mmwrhtml/rr4901a2.htm
Campaign Planks

Vaccine Protocols
Outlines vaccine protocols—including vaccination schedule, contraindications, precautions, recommended route, dose, and injection site—for influenza, Td, and zoster vaccines.

Standing Orders for Immunizations
Provides an example of a standing order policy and procedure.

Adult Seasonal Influenza Vaccine Standing Order
Shares an example of an influenza vaccine standing order to guide eligible nurses, medical assistants, and pharmacists in outpatient settings.
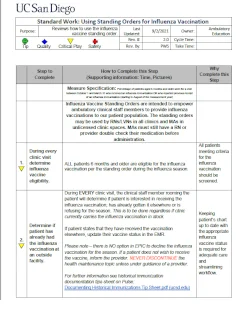
Steps for Using Standing Orders for Influenza Vaccination
Diagrams a workflow for utilizing standing orders to administer influenza vaccinations.

Steps to Implementing Standing Orders for Immunization in Your Practice Setting
Offers a step-by-step guide to integrate vaccination standing orders within practice settings. The comprehensive guide is divided into three phases: building support of leadership, developing materials and strategies, and implementing the vaccination program.

Standing Orders for Administering Hepatitis B Vaccine to Adults
Provides a sample standing order for administering hepatitis B vaccine to eligible adults. This document is intended to be adapted and adopted for use in a practice or clinic setting.

Standing Orders for Administering Influenza Vaccine to Adults
Provides a sample standing order for administering influenza vaccines to eligible adults. This document is intended to be adapted and adopted for use in a practice or clinic setting.

Standing Orders for Administering Pneumococcal Vaccines to Adults
Provides a sample standing order for administering pneumococcal vaccines to eligible adults. This document is intended to be adapted and adopted for use in a practice or clinic setting.

Standing Orders for Administering RSV Vaccine to Adults Age 60 Years and Older
Provides a sample standing order for administering the RSV vaccine to eligible adults. This document is intended to be adapted and adopted for use in a practice or clinic setting.

Standing Orders for Administering Td/Tdap Vaccine to Adults
Provides a sample standing order for administering the Td/Tdap vaccine to eligible adults. This document is intended to be adapted and adopted for use in a practice or clinic setting.
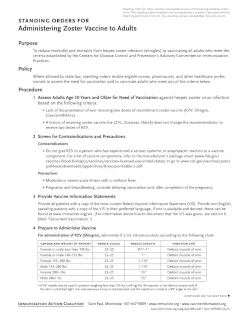
Standing Orders for Administering Zoster Vaccine to Adults
Provides a sample standing order for administering the zoster vaccine to eligible adults. This document is intended to be adapted and adopted for use in a practice or clinic setting.

"Using Standing Orders for Administering Vaccines: What You Should Know" Factsheet
Outlines the purpose, elements, and benefits of standing orders. This document is valuable for healthcare providers and staff considering implementing standing orders within their organizations.