Campaign Toolkit

Patient Education: Level 2
Conduct proactive outreach to patients
Identify target populations for proactive, tailored outreach. Leverage touchpoints and resources in the care delivery system and your community. Consider timing, budget, and other organizational initiatives in your planning and execution.
Conducting proactive outreach to your patients is critical to educate them about routine adult immunizations as well as drive desired behaviors, such as scheduling an appointment or getting a recommended vaccination. The following steps outline how to plan for and execute effective patient outreach. If your organization has access to a marketing/communications department, consider collaborating with them on the steps below.
Step 1:
Assemble a planning committee
Set up a planning committee to make important decisions about your approach to and goals of outreach and ensure adequate staff time and budget. Committee members typically include quality and population health leads but should also involve your Chief Quality Officer or Chief Medical Officer, as well as representatives from staff who will execute the plan (e.g., care coordinators, nurses, front desk staff).
Step 2:
Define your priority audience(s) for outreach
Identify your highest priority audiences for outreach. In addition to patient segments that you already have in mind or have identified through gap reports, consider targeting the following groups:
-
Employees of your organization, who can provide a strong vaccine recommendation to patients once vaccinated themselves
-
At-risk and high-risk patients, such as patients who are immunocompromised (high risk) and immunocompetent (at risk) and would benefit most from routine immunizations
-
Underserved groups, such as those that may be negatively impacted by social determinants of health or have historically low vaccination rates
Consider the schedules of providers who treat these patients and ensure that planned outreach doesn’t overwhelm their capacity. If you anticipate scheduling delays, start with a “schedule clean-up” to optimize visit times or triage your outreach accordingly.
Step 3:
Tailor messages
Determine the main message or call-to-action for each of the audiences identified for outreach. To maximize response, tailor your messages to specific vaccination types and patient populations and keep your messages direct and short. You may preliminarily test a few different messages to determine what works best for your target population.
Step 4:
Identify communication channel(s)
Identify what communication channels are available to you, and then determine what mix of channels will most effectively reach each audience. Consider channels that enable patients to take a desired action immediately, such as making an appointment over the phone or via a secure web page. Examine opportunities both within your care delivery system—like your patient portal or clinic website—as well as external resources—such as emails, text messages, and automated call systems. The right external resources and tools can help you reach your target populations where they live, work, and receive care.
As you plan, remember that each channel has special considerations. For example, to begin a text message program, you’ll want to ensure your patient intake forms specify and capture cell phone numbers versus home phone numbers. You’ll also want to consult your organization’s policies to determine what approval(s) you need to send patients text messages.
Step 5:
Determine frequency and timing of outreach
Consider frequency of outreach. If you send just one message via text, it might end up ignored or unread. Alternatively, several emails can overwhelm your patients. The right frequency of messages sent through two or more channels may be most effective.
Timing is also an important consideration. You may time your messages to align with seasonality (e.g., flu season), holidays, and tribute months, such as National Immunization Awareness Month in August. On a more granular level, if you are conducting phone or text message outreach, consider the best times of day to reach your patients.
Step 6:
Develop supporting tools
Identify existing resources (messages, emails) to support your outreach efforts as well as tools that need to be developed. Equip anyone conducting phone outreach with a standard script to keep calls on message. Also consider developing an FAQ sheet to help employees answer the most anticipated patient questions.
Step 7:
Execute outreach and modify as needed
Once you begin patient outreach activities, be sure to measure and examine outcomes and adjust tactics as needed. For example, if patients are not scheduling vaccination appointments in response to staff phone calls, consider revising your messaging to better resonate with that audience.
Campaign Planks

Flu Outreach Email Template
Provides a template email message for distribution to patients encouraging them to receive their annual flu vaccines.
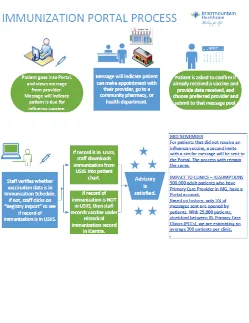
Patient Portal Process
Diagrams the outreach process via an organization’s patient portal to motivate patients to receive an immunization.

Flu Outreach Messaging
Offers example patient outreach to debunk common influenza vaccination myths. Includes a tailored message for African-American and Hispanic patients.

Flu Vaccine Reminder Patient Portal Message
Offers a template patient portal message for patients encouraging them to schedule and receive an annual flu vaccination.

"Adaptive Vaccination Solutions" Guidebook
Offers patient engagement materials and tools to improve communication about vaccines and help organizations achieve immunization success.